Acne & Acne Scars
Acne is the most common skin condition among teenagers and often persists into adulthood. In 20% of cases, it is moderate to severe.
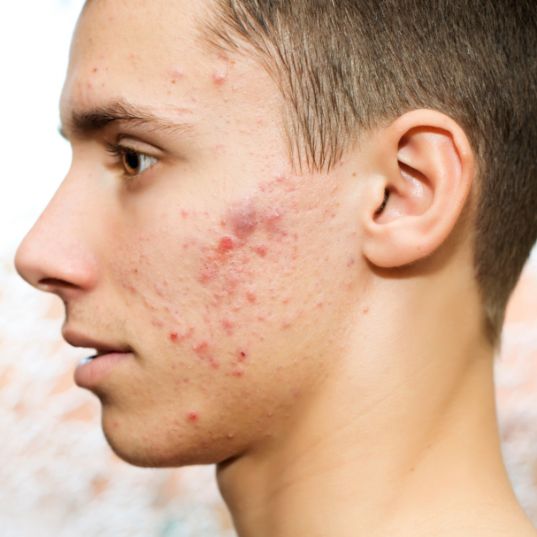
The severity of acne and the effectiveness of its treatment vary from person to person. Regardless of age, the main cause of acne is the excess production of an oily substance called sebum. Hormonal influence can lead to excessive sebum production and the development of acne.
The accumulation of dead skin cells, sebum, and bacteria leads to persistent redness and inflammation, particularly on the face, scalp, back, and chest, where sebum production is the highest. It is not always easy to predict which type of acne will leave marks, meaning scars. (Photo showing different types of acne: comedones, papules, pustules, nodules...)
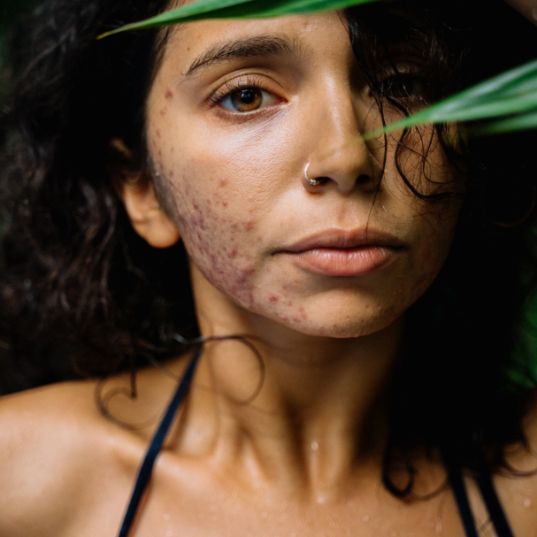

Genetic predisposition can contribute to its onset.
This means that acne is more common in certain families. Although it is not the direct cause, certain daily habits can worsen or contribute to acne outbreaks. For example, consuming certain foods, using unsuitable cosmetic products, stress levels, environmental pollution, and many other factors could contribute to acne.
Improving and Alleviating
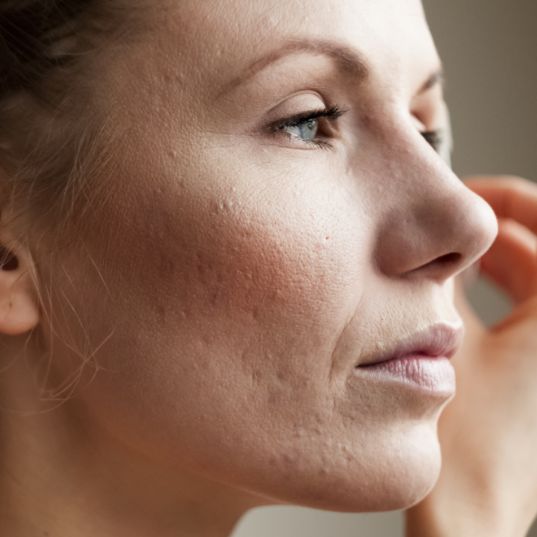

The goal in reducing acne is to reduce sebum production and calm inflammation. Certain daily practices can have a positive impact on your acne:
- Cleanse and moisturize your skin morning and night with products suitable for your skin type.
- Avoid traumatizing the skin by touching, squeezing, or scratching your pimples, as this increases the risk of scarring
- Do not expose yourself to the sun without protection (hat, high SPF sunscreen) as it can cause scarring.
Acne can significantly affect quality of life, which is why it is important to treat it. Without treatment, certain forms of acne can leave scars. (Photos of scars)
We can help you improve and better control your acne. Several solutions are available to reduce inflammation, calm the skin, and prevent scarring.
There are also topical and oral treatments that require a prescription and medical supervision. Consider consulting with your family doctor or a dermatologist recommended by your doctor.
